Introduction
Ego is an open-source, OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect compliant application that simplifies user management by providing methods to authenticate (establish who a user is) and authorize (establish what a user is allowed to do) users of your application through well-known social Single-Sign-On identity providers like ORCiD or Google. Ego provides stateless authorization using JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and can scale very well to a large number of users.
Features
Authentication
Ego allows users to login and authenticate themselves using the well-known and secure OAuth 2.0 protocol. Ego does not manage usernames and passwords, but instead relies on popular identity providers to complete this. Supported integrations include:
- Github
- ORCiD, a well established "research" identity passport
Ego also uses the OpenID Connect (OIDC) layer built on top of OAuth 2.0 to verify the identity of end users logging in from various providers and to obtain basic user profile information (such as first and last names, contact email address, etc.)
Authorization
Once users are authenticated, they are granted tokens that encode permissions to access resources. Ego supports:
| Type | Use |
|---|---|
| Application JWTs | For authorization of individual applications. |
| User JWTs | For authorization of individual users. |
| User API Key | For users to interact with applications registered in Ego using the level of authority as defined by the key. |
Secured applications can create and manage authorization tokens, and use those tokens to interact with third party applications registered in Ego to manage resource authorization. For more details on how tokens are used in Ego, see Tokens later below.
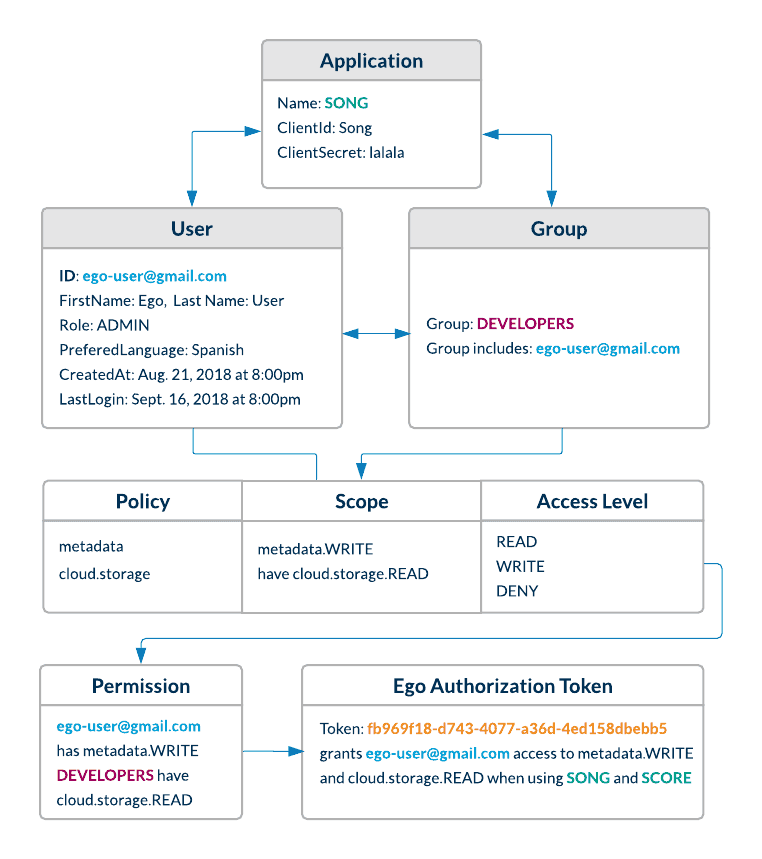
The actual permissions that can be granted are managed using Applications, Groups, or can be directly assigned to Users. To understand how these entities work together to provide authorization management, see How Ego Works later below.
API
Ego provides an API based on the OpenAPI specification (formerly known as the Swagger specification) which allows users (manually) and applications (programmatically) to interact with Ego's core functionality. One major benefit of Swagger-based APIs is that they also provide easy-to-use, interactive API documentation via a web interface. Users can manually interact with the API by issuing cURL commands via their terminal. Administrators with access to the Swagger UI can also interact with the API via the web interface. For more details about using the API, see here.
Admin UI
In addition to the comprehensive API, Ego is complemented by an administrative UI application to make user management even easier. For details on how to perform key user management tasks in the UI, see Using the Admin UI.
How Ego Works
Once Ego has been setup, Ego resolves a user or application identity with the permissions that they have been granted, either directly or inherited through a group. Permissions are encoded in a secret authorization JWT that has a limited life. This default expiry period is configurable during Ego setup.
Downstream services (for example, a research data portal trying to determine allowed actions for a logged-in user) must make a REST call to Ego to determine the user and authority represented by a JWT, or can accept a JWT and decide from the encoded information if a user or application is allowed to take a certain action.
The diagram below shows the relationship between the entities that work together to provide authorization and permission management in Ego:
Key Entities
| Entity | Description |
|---|---|
| User | A user is any individual registered in Ego who needs to authorize themselves with Ego-aware applications. |
| Admin | An admin is a power user whose role is set to ADMIN. Only admins are authorized to register users, groups, applications & policies using Ego’s REST endpoints. |
| Group | A group of users with similar properties. Admins can create new groups and add users to them. They can then assign permissions to an entire group which will be reflected for each user in that group. This greatly simplifies permission management for similar users, since the admin only needs to assign a permission to the entire group, instead of each individual user. |
| Policy | A policy is a scope or context for which an application may want to grant READ/WRITE/DENY permissions to a particular user or group. |
| Permission | A user or group can be given READ/WRITE/DENY permissions for a particular policy. |
| Application | An application is a third party service that registers itself with EGO so that EGO can authorize users on its behalf. Upon registration, the service must provide secure credentials in the form of a Client ID and Client Secret pair. |
| Application JWT | This is a basic JWT token which encodes a Client ID and Client Secret, and authorizes an application to interact with Ego. This is passed in the authorization request header when an application uses the check_token endpoint to check a user’s token. |
| User JWT | This is a Bearer token which encodes user information, and is passed to a user when they are authenticated through OAuth single sign-on. This Bearer token is passed in the authorization request header whenever the user wants to access Ego’s resources. If the JWT denotes that a user has an ADMIN role, they are permitted to create and modify resources (users, groups, permissions, policies). |
| User API Key | This is a random token which is generated to authorize a user for a specific scope, in the context of an application. Note that a user can have multiple active API keys, as long as they contain different scopes. |
Tokens
User Authentication tokens are signed JSON Web Tokens (JWT) issued when a user successfully logs into Ego using their login provider credentials. JWTs are an open, industry standard RFC 7519 method for statelessly representing claims securely between two parties, and are intended to be used as a Bearer token, passed as the Authorization header as part of any web request. Authentication establishes the identity, or who, a user is and as such authentication tokens are used to verify an application or user’s identity and contain information about the entity.
JWT data is current as of the time the token is issued, and the token is digitally signed by Ego with a publicly available signing key that applications have to use to verify that an authentication token is valid. Most of Ego’s REST endpoints require an Ego authentication token to be provided in the authorization header, in order to validate the identity before operating on data.
Application JWT
Application JWTs contain information about an applications's name, role (user/administrator), status, client credentials, and permissions (materialized as scopes) associated to an application. You can identify that it is an application token through the "application" block that is defined. An example of a user token issued by Ego is shown below:
{"iat": 1586974587,"exp": 1586985387,"sub": "593b93d4-30a0-4c0a-be9b-45d09d196a39","iss": "ego","jti": "1db416b6-4dee-4d1c-9c80-0798ad938694","aud": [],"context": {"application": {"name": "Song","clientId": "song","redirectUri": "https://song-example-redirect.com","errorRedirectUri": "https://song-example-redirect.com/404","description": "This is an integration between Ego and Song.","status": "APPROVED","type": "ADMIN"},"groups": ["69b77768-2016-4f04-802e-37334d823fd1"],"scope": ["*.DENY"],}}
User JWT
User JWTs contain information about the user's name, role (user/administrator), status, and any permissions (materialized as scopes), and groups associated with their Ego account. You can identity that it is a user token through the "user" block that is defined. An example of a user token issues by Ego is shown below:
{"iat": 1617732676,"exp": 1617743476,"sub": "25c24836-a924-4e47-b35d-5bec9690ff56","iss": "ego","jti": "016453d2-998e-4662-9b12-6baa208c34f8","context": {"scope": ["SCORE.READ","SONG.WRITE","SONG.READ","DMS.WRITE","SCORE.WRITE","DMS.READ"],"user": {"email": "jon.snow@gmail.com","status": "APPROVED","firstName": "Jon","lastName": "Snow","createdAt": 1617152136269,"lastLogin": 1617732676272,"preferredLanguage": null,"providerType": "GOOGLE","providerSubjectId": "908761298318094571857","type": "ADMIN","groups": ["d1b669cc-fd52-46d7-937b-0ff8be76e3d2"]}},"aud": ["dms"]}
User API Key
In addition to providing a user JWT, Ego can also issue a user-based API Key which can be used to verify a user’s permissions to execute on a desired scope.
An API Key is a random ID, issued by Ego to an individual user, so that they can interact with applications registered in Ego with a chosen level of authority. Each API Key is a unique secret password that is associated with a specific user, their permissions, and optionally, an allowed set of applications.
For example, a user would configure a client program (such as Song's command line client) with their API Key, and that program will subsequently operate with the level of authority associated with the API Key.